Technology
What is CTS technology?
Electric Green’s solution is made possible because we use the patented Capacitive Transfer System (CTS). It’s a self-compensating cable that delivers more of the input power than conventional cables.
Distribution of power through CTS results in far lower voltage drop than traditional Litz cables and enables us to design better, more efficient systems which other wireless providers struggle to do.
Conventional cable
CTS cable
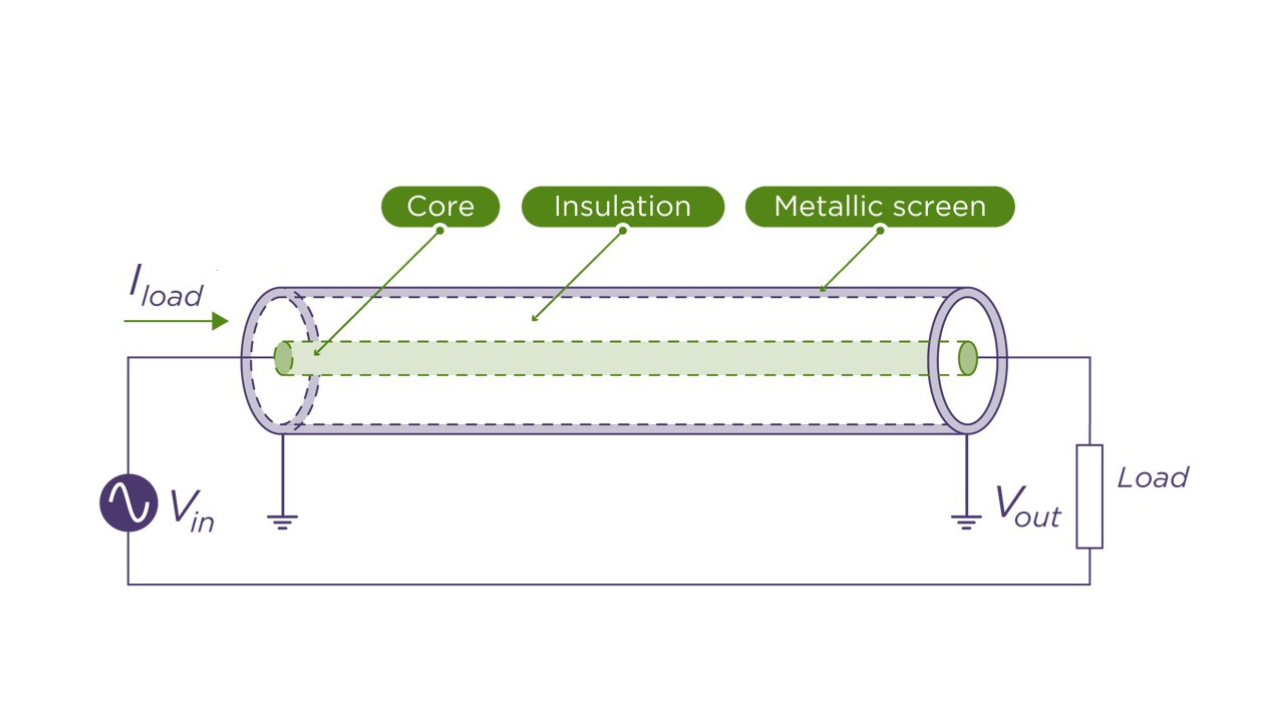
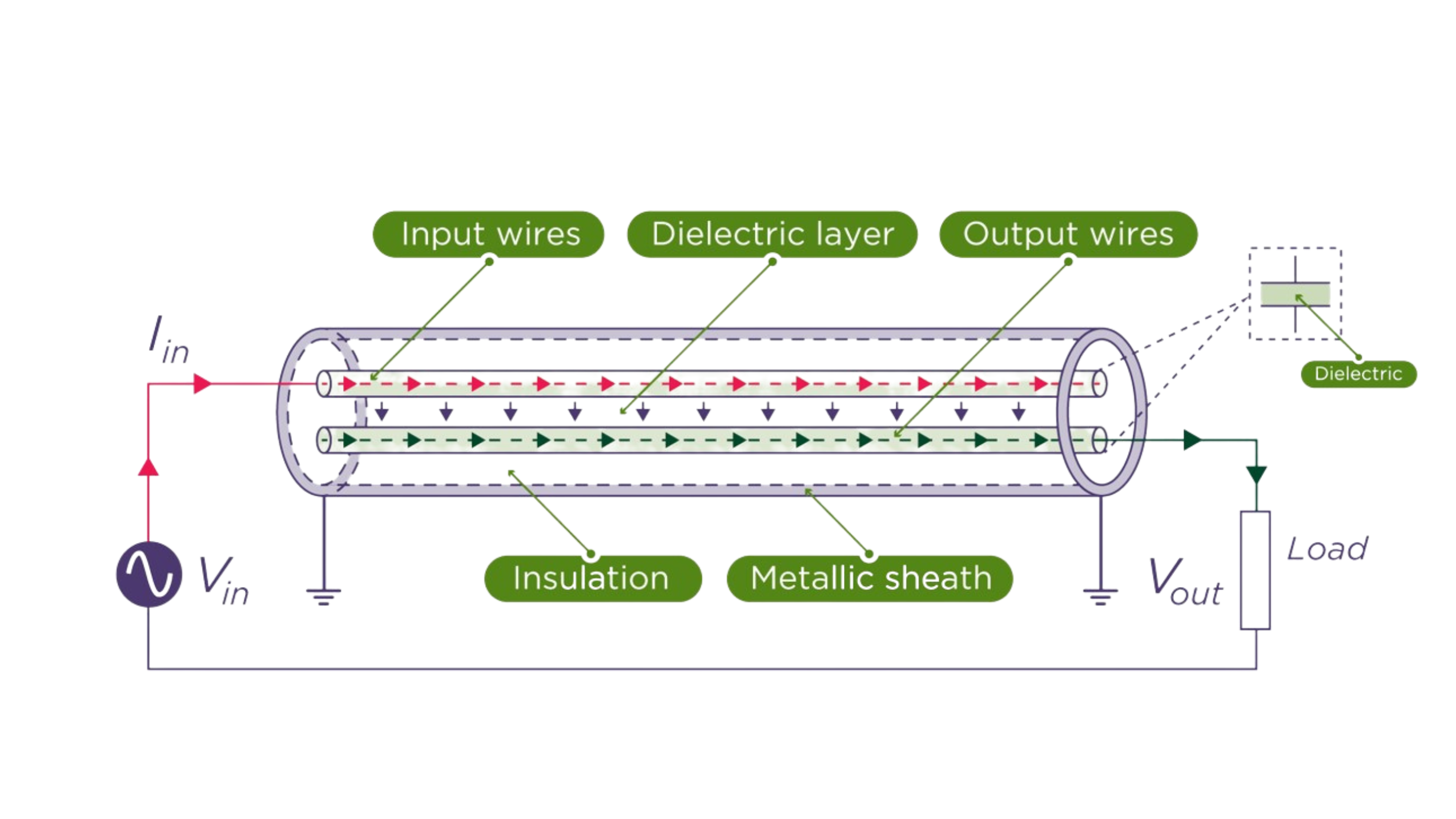
How does it work?
Specifically, CTS enables us to deliver the high frequency AC electricity (85kHz) used in Wireless Power Transfer (WPT) over long distance. At these frequency levels, reactance becomes the dominant component of the impedance. It is this reactance that CTS significantly reduces and hence why its performance is so superior and unique in WPT applications.


How does it work?
Specifically, CTS enables us to deliver the high frequency AC electricity (85kHz) used in Wireless Power Transfer (WPT) over long distance. At these frequency levels, reactance becomes the dominant component of the impedance. It is this reactance that CTS significantly reduces and hence why its performance is so superior and unique in WPT applications.

CTS benefits
For instance, in a comparison of a 100 metres sample of CTS and conventional cable using a stable 50 Amp current and 400 Volts, the conventional cable causes the voltage to drop by 65% at 85kHz whereas CTS only has a 5% voltage drop.
Put another way, by matching the design of the cable to a particular wireless charging application, it is possible to virtually eliminate the distance constraint associated with conventional cable.
These benefits are applicable to all wireless EV charging applications including static, semi-dynamic and dynamic scenarios.
Higher power capacity delivery
Lower capital costs

Lower operating costs

Efficient undergrounding

Reactive power support
Conventional cable vs CTS
No Data Found
The voltage drop for a conventional cable at 85kHz is 37% at 20m and more than 95% beyond 150m. By comparison, over a similar distance, CTS at 85kHz experiences only a 5% voltage drop.
